What Temp Does Beef Fat Melt
What is meat?
Every fourth dimension you lot stride up to your grill or into your kitchen, you begin a science experiment. As meat is heated, it undergoes physical and chemical changes, and equally scientific every bit these processes are, they are too magical. A basic understanding tin can help you melt juicier craven breasts and more tender steaks. This article is an overview and the links inside take yous to articles that explain the concepts in greater detail.
Meat is cut from the muscles of mammals and birds. For some reason, fish muscle is not considered meat by some people, but it should be.
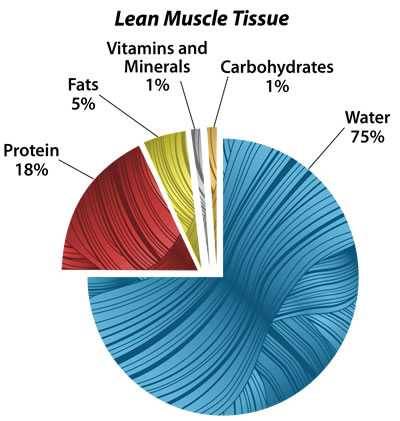
On boilerplate, lean muscle tissue typically breaks down like this: Water (nearly 75%), protein (xviii%), fats (5%), carbohydrates, salt, vitamins, sugars, and minerals (ii%). Here are some specifics.
| Animal | H2o | Poly peptide | Fats | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beefiness | 72% | 21% | 6% | one% |
| Pork | 69 | 20 | 10 | 1 |
| Chicken | 73 | 21 | 5 | i |
| Lamb | 73 | twenty | 5 | 2 |
| Cod | 81 | 17 | 1 | 1 |
| Salmon | 64 | 21 | 14 | 1 |
Unlike cuts from within an animal can differ significantly. As shown higher up, the average h2o content of pork is 69%. Pork rib meat, however, is more like 65% water, 18% protein, 15% fatty, and two% carbohydrates, salt, vitamins, sugars, and minerals. Even then, 65% is pretty high percentage of water. With that much water in the meat, any loss you might have from stabbing it with a thermometer or an occasional stab with a fork is minor, so don't allow the snobs tell y'all that you lot are going to ruin the meat if you employ a thermometer to bank check its temp or a fork to turn it. To illustrate: if you have an 8 ounce filet mignon, 6 ounces is water. Stab it and a few drops leak out from the puncture site, an insignificant part of the 6 ounces. Meat is not a balloon that goes phffffft and deflates when you poke it with a thermometer or fork
Muscle cells
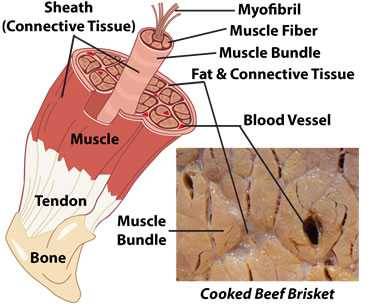
Muscle cells are more oftentimes chosen muscle fibers because they are shaped like tubes. Muscle fibers arranged together are called sheaths, and sheaths bundled together are chosen muscle or meat.
The fibers, virtually the thickness of a human pilus, contain several types of protein, among them myosin and actin which bind upwardly water and act like living motors by contracting and relaxing on command. As an animal ages, grows, and exercises, its muscle fibers go thicker and tougher. And muscles similar shoulders and legs get thicker and tougher than the smaller, more tender muscles call "tenderloins" that run forth the animal's spine.
Myoglobin is some other important protein in musculus fibers. Myoglobin receives oxygen and iron from hemoglobin in claret, fuel necessary for muscles to role. Myosin and actin are not water soluble, but myoglobin is water soluble, and myoglobin dissolved in h2o is the pink liquid nosotros see seeping out from a package of raw meat or spilling onto the plate when we cutting into cooked meat. Myoglobin is the protein in meat that makes information technology announced red. On average, beef has 8 milligrams of myoglobin per gram of meat, co-ordinate to the meat scientists at Texas A&Chiliad University's Section of Fauna Science, making it ane of the darkest red meats. Lamb has almost half dozen milligrams per gram, pork about ii mg/g, and chicken breast about 0.five mg/g.If pork is the other white meat, lamb is the other red meat (click here to share this fleck of wisdom on Twitter). When warmed, meat juices containing myoglobin lose their red color, become lighter pink, and somewhen tan or gray. Muscle fibers too contain other proteins: enzymes. Enzymes play an important role in aging meat.
Connective tissue
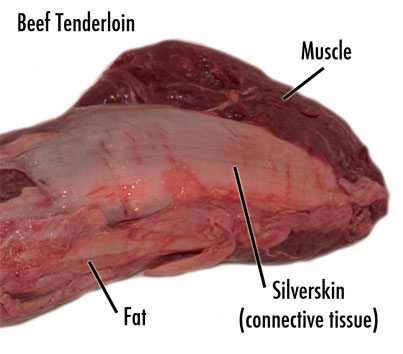
Connective tissue is most obvious in the form of tendons that connect muscles to bones and in ligaments that connect bones to other basic. It is also visible as the sparse shiny sheathing that wraps around muscles called silverskin or fascia. These tougher, chewier, rubberband-similar connective tissues are generally collagen and elastin (as opposed to the muscle, which is more often than not myosin.) We call them gristle and they shrink when heated and get difficult to chew. As with muscle fibers, connective tissues thicken and toughen every bit an animal exercises and ages.
A softer connective tissue called collagen is scattered throughout the muscle, often surrounding fibers and sheaths holding them together. When y'all cook, collagen melts and turns to a rich liquid chosen gelatin , similar to the stuff Jell-O is made from. Cooked muscle fibers, no longer bound together past collagen, are at present uniformly coated with a soft, gelled lubricant. This smoothen and sensual substance enrobes meat in a wonderfully silken texture and adds wet. And yes, this is pretty much the same stuff the Hollywood wives have injected into their faces to go rid of wrinkles.
Lean meats similar beefiness or pork loin and tenderloin, equally well as nigh chicken and turkey, don't have much collagen. When cooking tough cuts of meat with lots of connective tissue, like ribs, brisket, and shoulder, it is important to liquefy the meat'southward connective tissue into gelatin: that's what makes these tough meats taste tender. This takes time. That'south why these cuts are often cooked low and ho-hum. Muscle fibers showtime seizing upwards around 125°F to 140°F if heated speedily. Just when heated slowly, the rubber ring-similar connective tissues accept fourth dimension to relax and exercise not squeeze tightly. In general, information technology is best to cook all meats at most 225°F. Tedious roasting does wonders for meat. The AmazingRibs.com science advisor Prof. Greg Blonder says "Think of giddy putty. Pressed hard and rapidly, it acts similar a rigid solid. Pressed slowly, it flows." When heated slowly, the muscle fibers, instead of wringing out moisture, relax and simply let water linger inside until evaporation drives it out.
Afterward it melts, as it chills, gelatin tin solidify into that jiggly stuff which, with a little filtering, tin can then be called aspic and served at span clubs. Hither'due south a pot of the stuff fabricated simply by boiling a couple of chicken carcasses in water after I ate the meat, discarded the bones, and chilled the liquid. The white is fat, most of which I take removed, and the tan is jiggly gelatin.

Fats
Fats (lipids) and oxygen are the main fuels that ability muscles. Fats are packed with calories, which are potential energy released when the chemical bonds are broken. From a culinary standpoint, fat comes in three types (encounter the photo at the top of the page):
- Subcutaneous fats are the thick difficult layers beneath the skin.
- Intermuscular fats are layers betwixt muscle groups.
- Intramuscular fats woven amongst the muscle fibers and sheaths meliorate meat's moisture, texture, and season when cooked. These threads of intramuscular fatty are called marbling because they have a striated expect like to marble.
Large fatty deposits tin also be constitute around organs, especially kidneys. On hogs, the best fat of this type, at least from a culinary standpoint, peculiarly if you make pie crusts, is called leaf lard, and information technology comes from around the kidneys.
Fats are crucial to meat texture. Waxy when cold, fats start to melt around 130°F to 140°F, lubricating muscle fibers just as they are getting tougher and drier from the heat. Fat does non evaporate similar water when you are cooking.
Fatty also provides much of the flavor in meat. It absorbs and stores many of the effluvious compounds in the animal's nutrient. As the fauna ages, those flavor compounds build upward and get more than noticeable. Afterwards the brute is slaughtered, the fat can turn rancid if stored also warm, likewise long, or in contact with oxygen. And then we take a tradeoff. The muscle fibers and connective tissues get tougher as the creature ages and exercises, while the fatty accumulates and builds flavor.
Fats, particularly animal fats, are the subject of great debate among scientists, doctors, dietitians, and health faddists. For many years, brute fats were thought to exist dangerous and avoided. Information technology is now thought that fats, even animal fats, contain many beneficial components, and electric current science argues that, in moderation, they are essential for health. A great bargain of interesting research on the subject field is going on as I blazon this. A great deal of research is contradictory. Read more about what I have learned about food and health in this commodity.
Fluids
Most of the liquid in meat is water. The carmine color in meat and its juices is not acquired past claret. It is the poly peptide myoglobin dissolved in water. Myoglobin is found only in musculus, non in the blood stream. The blood is pretty much all drained out in the slaughter business firm. If the stuff on your plate when yous sliced a steak was blood, it would be much darker, like human blood, and it would coagulate, like human blood. If the fluids were claret, then pork and craven would be dark red. It's mostly merely h2o, and so let's end grossing out our kids, and simply telephone call it juice. OK?Every fourth dimension you call meat juices claret, a bell rings and a teenager becomes a vegan.Click hither to Tweet this fleck of wisdom
When animals are live, the pH of the muscle fibers is about 6.8 on a scale of 14. The lower the number, the higher the acidity. The higher the number, the more alkalinity and less acidic. At half dozen.8, living musculus is simply near neutral. When the animal dies, the pH declines to about v.5, making it acidic. At this pH, muscle fibers form bunches and clasp out juice, called purge, and that is the juice you see in packages of meat that is absorbed by the diapers they put under the meat.
Slow twitch vs. fast twitch muscles
Musculus fibers demand fat and oxygen for fuel. Fat comes from fatty acids in the animal's blood that were created by digestion of its food. Oxygen is carried by the protein hemoglobin in the bloodstream, and it hands the oxygen to myoglobin inside the muscles.
In full general, the more exercise a muscle gets, the tougher it is, and the more oxygen-laden myoglobin information technology needs. Myoglobin turns meat darker and makes it more flavorful. Nighttime meats, like craven thighs are made of "slow twitch" muscles that have evolved to endure slow, steady movement, and they are loaded with juicy myoglobin. White meats, like craven breasts, are mostly "fast twitch" muscles, which are better suited to brief bursts of free energy, and they accept less myoglobin. Dark meats also have more fat for energy.
When cooked, the slow twitch muscles in night meat have more moisture and fat and are more flavorful than white meat. White meats contains less moisture and fat, and they dry more hands when cooked. The legs and thighs of chickens and turkeys are proficient examples. These animals get more practise standing and walking than flying, so the legs and thighs have lots of slow-twitch muscles, more pigment, more than juice, more fat, and more flavour. They are also slightly more forgiving when cooked. Modern chickens and turkeys take been bred for large breasts because white meat is more pop in this country (and I for one, tin can't understand why). I'll take tough and flavorful over tender and mild whatever day.
[Like what you're reading? Click here to get Smoke Signals, our monthly e-mail that tells y'all about new articles, science, recipes, product reviews, and more. Be Amazing!]
Ducks and geese excel at flying and swimming, and they get more exercise than chickens and turkeys, so these birds have more dark meat. Duck breasts are deep imperial, nigh the same colour equally lamb or beef.
When the conventional wisdom was that dietary fatty could cause heart and arterial problems, domestic pigs were bred to take less intramuscular fat. The mod sus scrofa does not get much practise due to its transmogrification into "the other white meat." In contempo years, research has questioned the relationship between dietary fat and health, and many experts extol fat'due south benefits.
Beef is all pretty much the same color, but slow twitch muscles like flank steak have bigger, richer flavor than some of the lesser used muscles like tenderloin.
Fish live in a practically weightless surroundings, so their muscles are very unlike. Fish muscles have very little connective tissue, and that's one reason why fish never gets equally tough as pork when cooked. But fish can dry out because in that location is non much collagen to moisturize the musculus fibers. The color and texture of fish varies depending on the life it leads. Modest fish that swim with quick darting motions take mostly fast-twitch muscles and white meat, while flounder, which lives on the body of water floor, has delicate flaky mankind. Torpedos like tuna and swordfish swim long distances with dull steady tail movements, so they have take firmer, darker, sometimes even red flesh. For these reasons and others, fish tin spoil within days of being caught, while red meats keep much longer.
Brown is beautiful, black is bad

As meat cooks, the most magical transformation that occurs is the Maillard reaction. It is named for a French scientist who discovered the phenomenon in the early on 1900s. The surface turns dark-brown and crunchy and gets ambrosial in aroma. Who doesn't dearest the crispy outside of a slice of roast beefiness, the browned chaff on freshly broiled bread, or the crackling surface of a roasted marshmallow? We don't think twice about it, only that brown colour on the surface is the mark of hundreds of compounds created when heat, especially heat above 300°F, starts changing the shape and chemic structure of the amino acids, carbohydrates, and sugars on the surface of the meat. Click here to acquire more virtually the Maillard reaction and caramelization.
What you don't want is black meat. Let it become too far and information technology turns to carbon. Carbonized meat may be unhealthy.
Pretty in pinkish
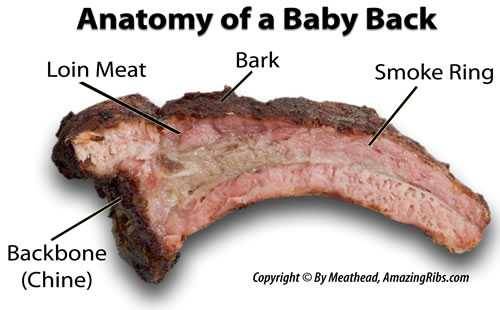
At that place's another color you may notice in cooked meat: pink. Many smoked meats turn bright pink only under the surface. Some people call up that pink color means that meat is raw, but not in this case. If the meat were undercooked, the pink would be in the centre, not just below the surface. Pink meat near the surface is a common phenomenon called the smoke ring and information technology is acquired by gases in smoke preserving the colour of myoglobin. Some people call up the smoke ring improves sense of taste. That's a myth besides. Click here to read more virtually the smoke ring and what causes it.
Cook with a thermometer, non a clock
Different cuts of meat vary significantly in tenderness, fat content, and collagen content. Some are best cooked hot and fast, some better cooked depression and tedious, and some must be cooked with a combination of hot and irksome to reach their optimal taste and texture. Click here to read an article on the subject field of cooking temps.
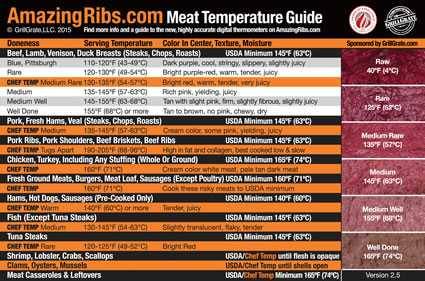
This is why cooking times are guesstimates at all-time. Think nigh the absurdity of a recipe that says, "cook the steak for six minutes on the first side and so four minutes on the second side." How long it takes to cook depends on how hot the air and the cooking surface are, how thick the meat is, and your target temp. Depending on the grill, cooking steaks could take twice equally long or half as long. Thick steaks take more than fourth dimension, and if you want them rare, they'll accept less time than in if you lot want them well done. Click here for more on cooking times and what controls them.
You lot cannot tell if meat is safe or cooked to the proper temp past looking at it. When y'all cut into meat to wait at information technology, information technology tin can change in a few minutes after information technology has been exposed to oxygen. Compounds in marinades and brines can affect color. Sometimes vegetables in the grill can produce gases that alter meat colour. It has long been idea that when chicken juices run clear the meat is rubber, merely modern chicken farming has changed that. Utilise a thermometer. Click here to read how we bust the myth of clear chicken juices.
The truth is, meat tin get from succulent to sucky in just a few minutes. The only way to be certain almost doneness is to use a digital thermometer. Overcook meat and yous've wasted your coin. Undercook it, and yous could give someone a tummy ache or much worse.That is why you Ever cook with a thermometer, not a clock. This is the 21st century. The digital age. Cease using 19th century applied science. Ditch your punch telephone and your dial thermometer.
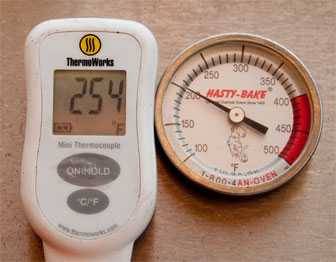
And while you are at information technology, get a digital oven thermometer. The cheap punch thermometer that came on your grill or smoker is probably off by 25 to 50°F like the ane higher up. I have seen them off by 100°F!
Click this link for a buying guide to thermometers with more than than 150 test results from our on-staff electric engineer.
Equally the internal temp of meat climbs, more water gets squeezed out, and the meat becomes drier. In general, most meats are juiciest when cooked to medium rare, 130 to 135°F internal temperature.
Simply that's not hot plenty for safe in some meats. Ground meats and poultry are wellness risks at those temps. Ground meats need to exist cooked to 160°F, and poultry needs to go to 165°F to kill pathogenic bacteria. But at that place's more than to the story than that. You tin actually serve these meats at lower temps if you lot know the rules. Read my article on meat temperatures.
Meats with a lot of connective tissue such as beef and pork ribs, pork shoulder, and beef brisket, are too tough at these lower temps. They need to go up to 200 to 205°F in society to gelatinize collagens and melt fats. That'due south well past well done, and yes, water is lost, but the gelatin and melted fats lube the meat and brand information technology taste tender and juicy.
Be aware that if you let meat sit around afterwards you remove it from the heat, the rut built up in the outer layers will button down to the center and overcook the meat, a process chosen carryover cooking. The good news is that resting meat is probably not necessary, despite what all the Idiot box chefs say. For more near ideal serving temps, read my detailed Nutrient Temperature Guide, which has a handy printout for your fridge.
What happens when you cook?
Hot air cooks the surface of meat, but it cannot penetrate, so the energy built upwards on the outside of the meat moves slowly towards the center, somewhen cooking the meat throughout. As the internal temp of your meat rises, its color is not the just thing that changes. A number of chemic and concrete reactions accept place, as the molecular structure of proteins and fats are altered by heat. Unlike reactions kick in at dissimilar temperatures.
0°F (-18°C). Ideal freezer temperature.
25°F (-4°C). Meat freezes. Meat starts to freeze at a lower temperature than h2o because water in meat is combined with proteins. Water expands as it freezes and sharp-edged crystals form that can rupture prison cell walls, creating "purge" when the meat is thawed, which is a spilling of liquid, generally the pinkish fluid poly peptide chosen myoglobin. Faster freezing makes smaller crystals, resulting in less purge.
32°F (0°C).H2o freezes.
34-39°F (1-iv°C). Ideal refrigerator temperature. Water is not frozen, and microbial growth is minimized. You practise accept a practiced refrigerator thermometer don't you?
41-135°F (5-57°C). The "USDA Danger Zone," in which many pathogenic bacteria grow, sometimes doubling in number in every bit fiddling as 20 minutes. According to the USDA, cold foods must exist stored beneath 41°F (5°C), and hot foods above 135°F (57°C). That's why we don't leave meats sitting around to come to room temp.
sixty°F (xv°C). When chilling cooked meat, liquid gelatin forms a solid gel called aspic. Gelatin happens when connective tissues that wrap muscle fibers and connect them to bones, called collagen, melt. Yep, it's the aforementioned stuff they inject under your skin to hibernate wrinkles.
95-130°F (35-54°C). Animal fats start to soften and melt.
114°F (46°C). Myofibrillar proteins begin to gel, changing meat texture.
120°F (49°C).Myosin, a protein involved in muscle contraction inside fibers, begins to lose its natural structure. It unwinds or unfolds, a process called denaturing. Information technology starts to clump, gets milky, and begins firming upwardly the muscle fibers. Purple meats, called "rare," kickoff turning crimson. Fish begins to flake, and parasites begin to dice.
130°F (54°C). Many pathogenic bacteria brainstorm to die, slowly at starting time, but every bit the temp rises, they croak more rapidly. At this temp, information technology takes more two hours to pasteurize meat. At 165°F (74°C), information technology takes just seconds.
130-135°F (54-57°C). Medium rare. Most mammal meats are at optimum tenderness, flavor, juiciness. If you swallow your meat well-done, you need to snap out of information technology.
130-140°F (54-60°C).Fats begin to liquefy, a process called rendering. This is a tiresome process and tin accept hours if meat is held at this temp.
140°F (60°C). Connective tissues chosen collagens begin to contract and squeeze out pinkish juice from inside muscle fibers into the spaces between the fibers and out to the surface. Meat begins to go dry. Myoglobin, the pinkish protein liquid within muscle cells, denatures rapidly and blood-red or pinkish juices begin to turn articulate or tan and dewdrop upward on the surface. It is not claret!
150°F (66°C). Actin, another poly peptide important to muscle contraction in alive animals, begins to denature, making meat tougher and drier however.
150-165°F (66-74°C). This is "the stall zone," in which large cuts such every bit pork barrel and beef brisket seem to get stuck for hours when cooked at low temperatures similar 225°F (107°C). In this range, wet evaporates and cools the meat similar sweat on an athlete. Inexperienced cooks panic. Eventually, temps start rising again. Whew!
155°F (68°C). Known as "well washed," meats are overcooked at this internal temperature. Much moisture has been squeezed out, and fibers take become tough. Leaner are killed in less than 30 seconds, but spores can survive to much higher temps.
160-165°F (71-74°C). The "instant kill zone." Normal cooking temps kill microbes on the outside of meats quickly, so solid muscle meats are not likely dangerous since contamination is well-nigh always on the surface. But ground meats and poultry often have bad guys beyond the surface, so you must cook these meats beyond the instant kill zone. That's why the recommended internal temp for footing meats is 160°F (71°C) and for poultry is 165°F (74°C). When you reheat foods, you should have them up to 165°F 75°C).
160-205°F (71-96°C). Tough collagens melt and form luscious gelatin. The process can have hours, so depression and slow cooking creates the well-nigh gelatin. Dehydrated muscle fibers begin to fall apart and release from the bones. Meat becomes piece of cake to shred. Even though the fibers have lost a lot of water, melted collagen and fatty make the meat delicious.
212°F (100°C). Water boils at sea level. Humid betoken declines about 2°F for every 1000′ above sea level.
225°F (107°C). Ideal air temperature for "low & slow" cooking of meats loftier in connective tissue. It is loftier enough so water evaporates from the surface to help form the desired crust chosen "bawl," just low enough to get the most out of enzymes, collagen melting, and fatty rendering.
230-234°F (110-112°C). Table sugar melts and pulls into a thread but will not class a brawl (thread stage).
300°F (149°C). Butter starts to smoke.
310°F (154°C). The Maillard reaction accelerates surface browning, which is acquired by chemical changes in proteins and sugars and results in thousands of delicious new molecules. The Maillard reaction begins at lower temps, but really takes off at 310°F (154°C).
320°F (160°C). Table carbohydrate liquefies, starts to caramelize, turns calorie-free amber in color (articulate liquid phase).
325°F (163°C). Ideal air temperature for cooking chicken and turkey and so pare browns and fat renders.
350°F (177°C). Table sugar and brown sugar brainstorm to burn down (burnt saccharide stage).
361°F (183°C). Some creature fats begins to smoke.
375°F (191°C). Extra virgin olive oil begins to smoke.
400°F (204°C). Canola oil begins to smoke.
425°F (218°C). Teflon thermometer cables can begin to melt.
440°F (227°C). Inexpensive olive oil begins to smoke.
450°F (232°C). Peanut oil begins to smoke.
450°F (232°C). Some nonstick surfaces begin to emit toxic gases.
570-750°F (299-399°C). Primary combustion temperature of hardwood, wherein it smolders and releases large quantities of unburned gases, including microscopic particles called fume.
600-700°F (316-371°C). Flash signal or fire point, the temperature at which smoke from burning fat can burst into flame. Never apply water to extinguish burning fat. Smothering it works better.
1110°F (599°C). Secondary combustion of wood when gases, cellulose, and lignin burn down quickly.
What causes properly cooked pork and poultry to be pinkish, even if it is not smoked?
Several factors: Gases in the temper of an oven, peculiarly carbon monoxide, can react with myoglobin in meat and turn information technology pink, especially on the outer edges. These gases occur in all ovens, especially those that estrus by combustion such as gas, charcoal, or forest. They are also present in electric ovens, but to a much lesser degree. When grilling or smoking, at that place are more of these gases. They more than easily penetrate the thinner skin and fat layers of younger animals, and then age of the animal is also a factor.
Besides, meats with high levels of naturally occurring compounds such as myoglobin are more likely to turn pink. Nitrites in meat can likewise cause pinking. Nitrites are converted from nitrates in feed and h2o by microorganisms inside the animate being. Nitrates naturally occur in many leafy vegetables and can transfer to the meat during cooking, say, from a rub or braise. In fact, grocery store meat trays are occasionally packed with carbon monoxide or nitrogen to keep the meat in the pink.
Why is raw carmine meat sometimes bright red on the outside and irksome grayness on the inside?
Fresh cut or footing beefiness is purplish-red in color. Oxygen reacts with the pigments in red meat to form the bright cherry-red colour in the grocery shop. The interior of the meat may be gray or chocolate-brown because oxygen has not penetrated into the muscle. This is normal. If, however, all the meat in the package has turned greyness or brown, it may be spoiling.
What is spoilage?
In that location are two types. Oxidation is caused by compounds in meat combining with oxygen and changing the meat's aroma, flavour, and color. Badly oxidized meat is called rancid. Merely oxidized meat is usually non unsafe. The other blazon of spoilage is bacterial or viral spoilage, and information technology is very unsafe. There are several commonly occurring bacteria in nutrient that can spoil it, such every bit are Bacillus cereus, Campylobacter jejuni, Clostridium botulinum, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella, Shigella, Staphylococcus aureus, and STECs (Shiga toxin producing East-coli). Some of these bacteria will merely accept you kneeling before the porcelain god, but others can maim or kill y'all. You lot tin brainstorm killing leaner by cooking food to a safe temperature of 131°F or higher. At 165°F, bacteria are killed instantly. At 131°F, it tin take hours. For more on bacterial kill temps, click hither and roll down.
Why is meat in my fridge is turning brown?
At first, oxygen reacts with pigments to turn meat red. After a while, the meat starts to oxidize, which turns it brown, the aforementioned way an apple or potato turn chocolate-brown.
Why does my meat shine similar a rainbow?
It is simply a fluke of lighting that strikes the surface merely the right style when the surface has been cut on a certain angle. Strictly refraction, not leaner or an oil slick.
Why is my meat light-green?
Bad bacteria. Throw it out.
Why are in that location are dry out white spots on my meat from the freezer?
That'southward freezer burn down. Information technology's like frostbite. The meat has probably been in the freezer as well long and/or it was non wrapped tight. It is still safe, but the burned parts will probably exist dry and banal. Trim information technology off and cook it, only don't serve information technology to Mom or the boss.
My meat smells funny, what should I exercise?
Sometimes meat will smell a fleck odd when you lot take it out of a vacuum sealed plastic bag, but the smell should dissipate within a few minutes. If it still smells funny, so chances are it is funny. Throw it out. Remember: when in doubt, throw information technology out!
What are those boogers coming out of my burgers and my salmon?
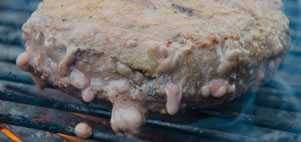

According to the AmazingRibs.com meat scientist, Dr. Antonio Mata, hamburger exudates (I call them boogers) are proteins dissolved in water, mostly myoglobin. When burgers are ground, plump muscle fibers are sheared open. Equally the meat begins to rut, poly peptide and collagen compress and clasp out the proteinaceous fluids, which are pinkish at first, and and so they gel and turn tan just like the meat.
Source: https://amazingribs.com/technique-and-science/cooking-science/basic-meat-science/
0 Response to "What Temp Does Beef Fat Melt"
Post a Comment